I. Product Introduction
- General Function and Purpose
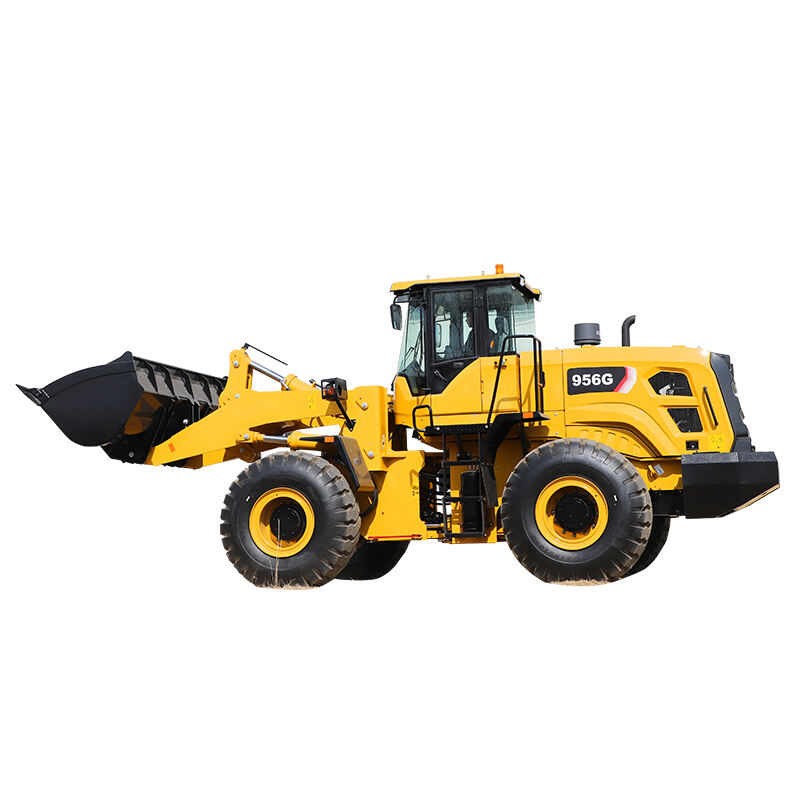
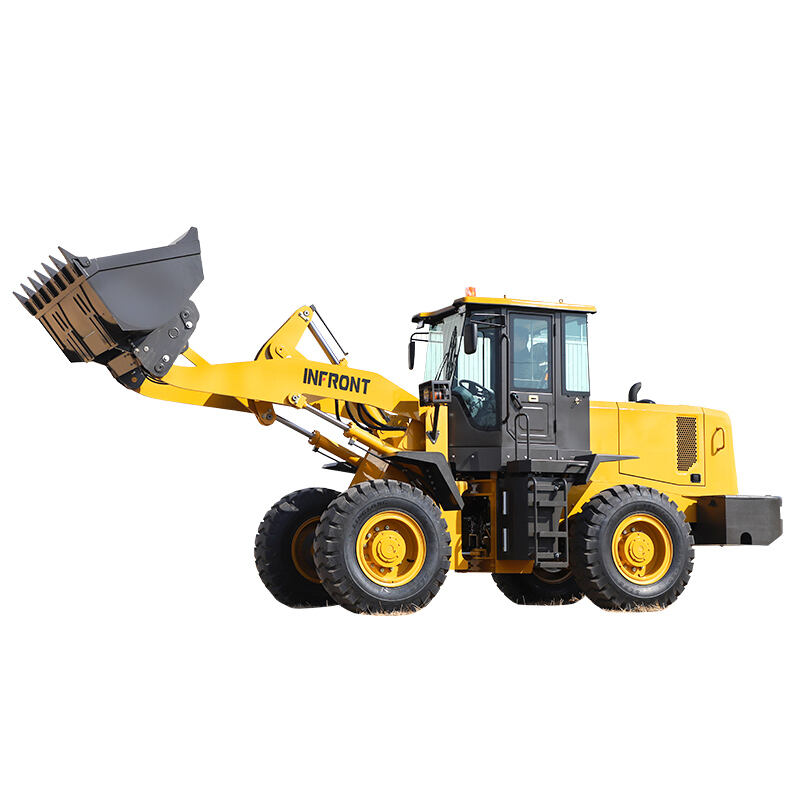
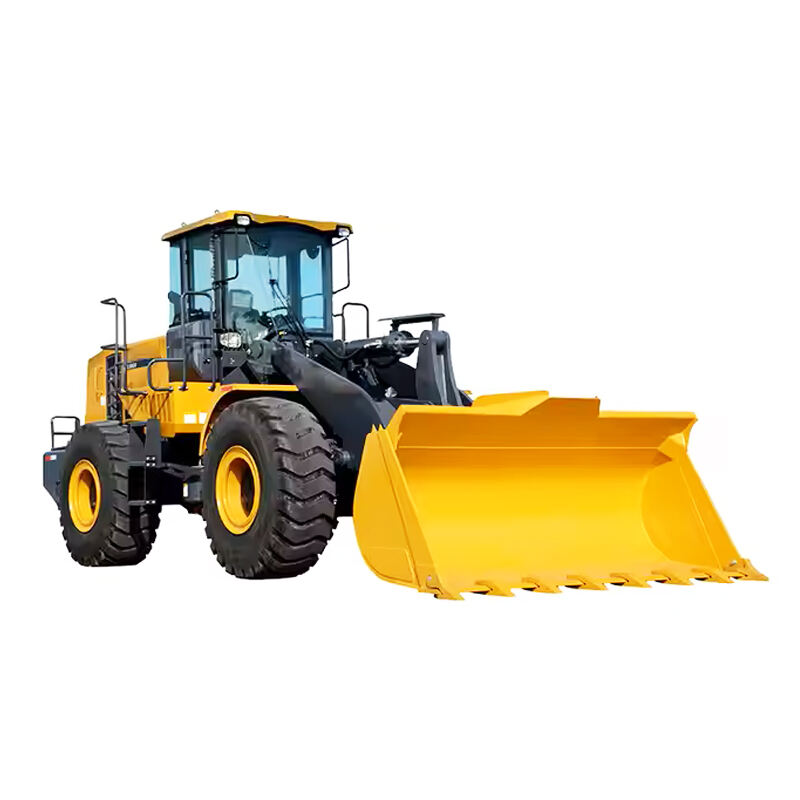
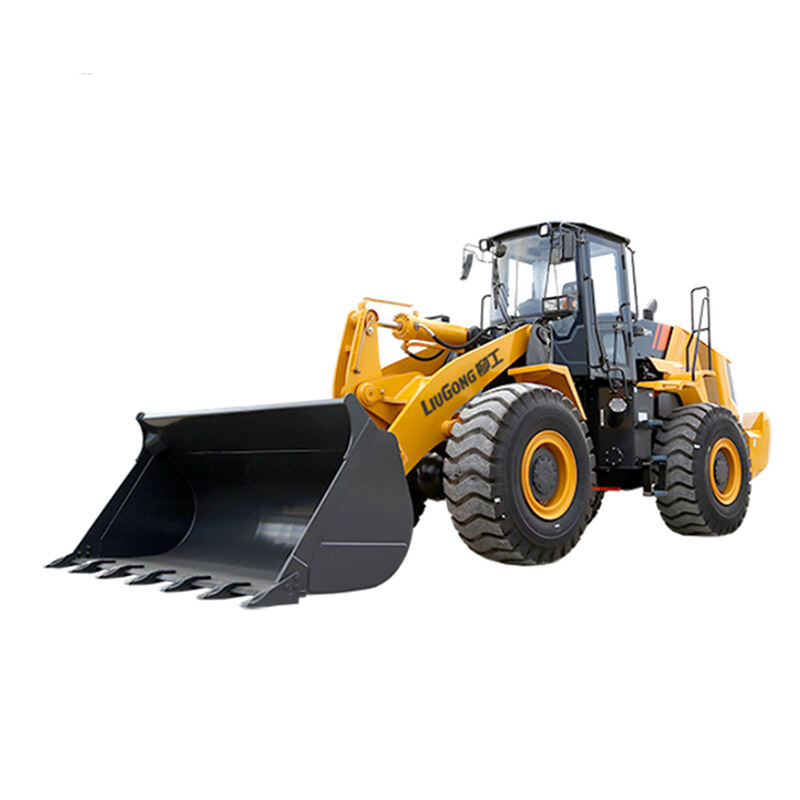
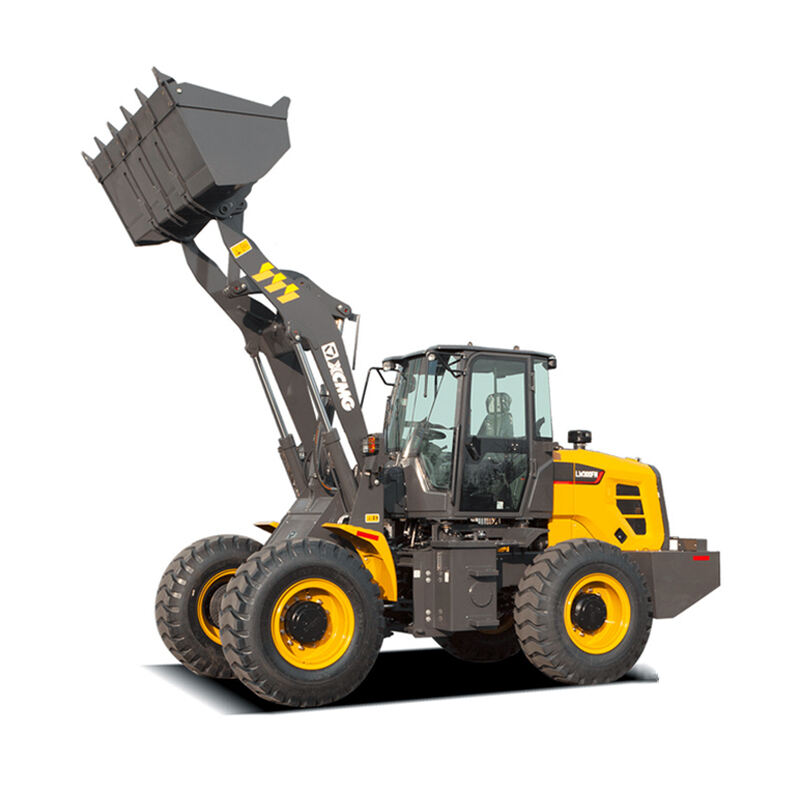
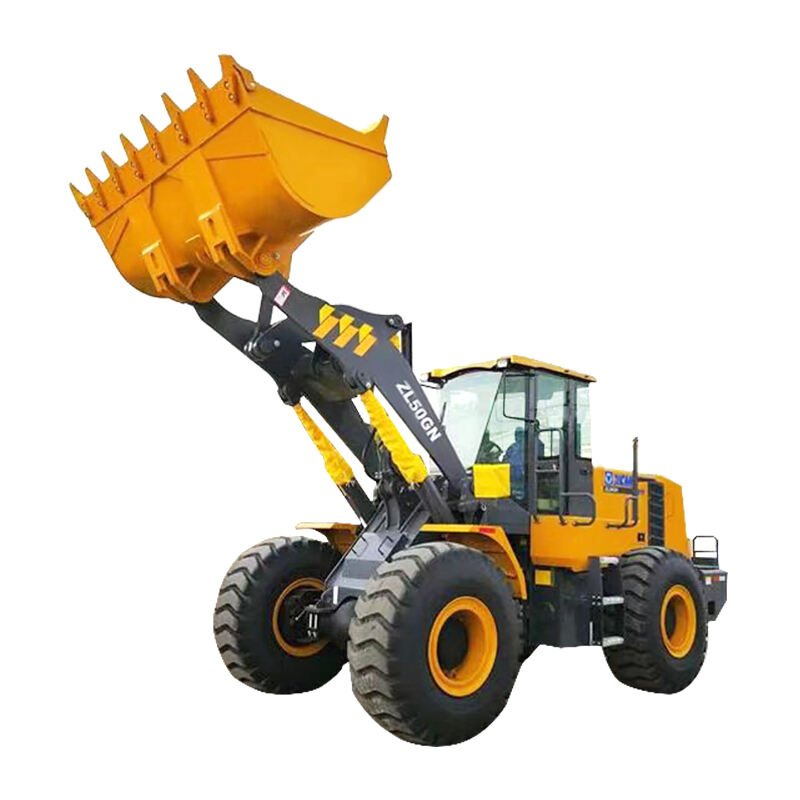
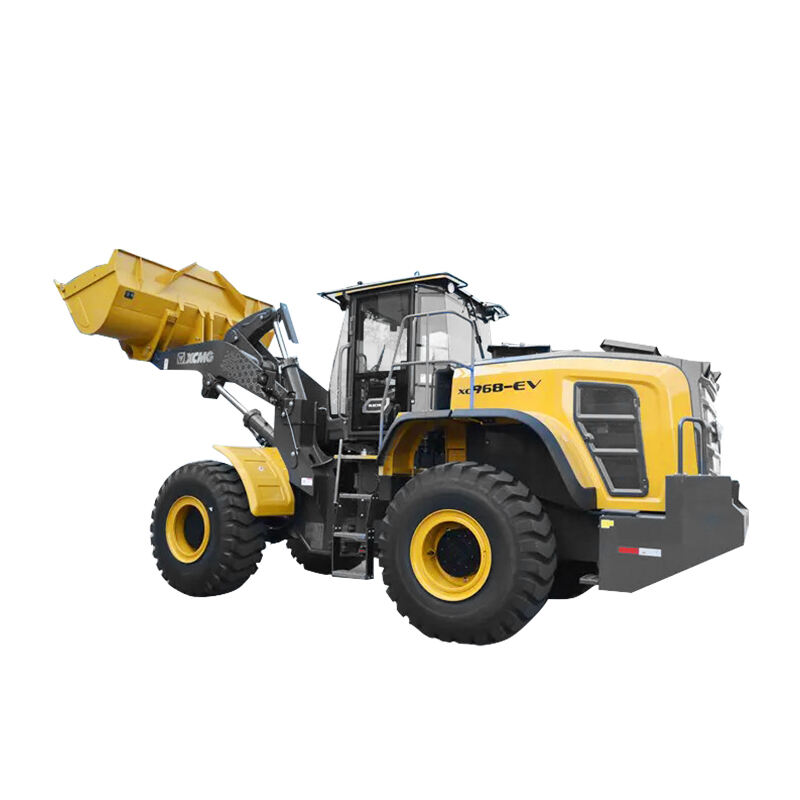
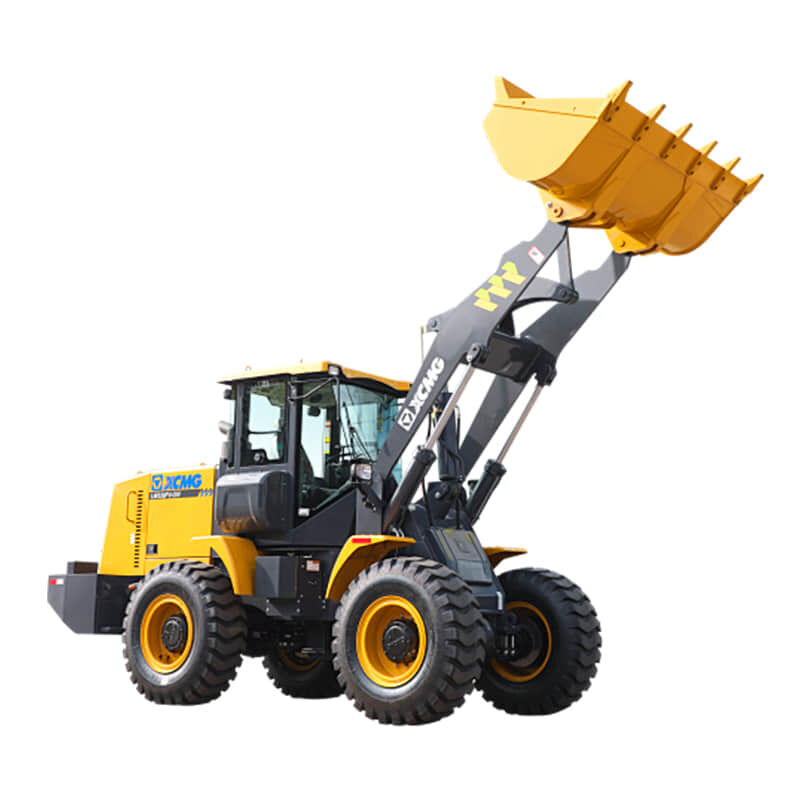
Wheel loaders are versatile heavy machinery widely used in construction, mining, agriculture, and many other industries. They are primarily designed to load and transport various materials such as soil, gravel, sand, and even bulky items like logs or rocks. With their efficient loading mechanism and mobility, they play a crucial role in facilitating the smooth progress of different projects.
- Key Components and Structure
The main components of a wheel loader include the chassis, engine, bucket, lift arms, and wheels. The chassis provides a stable base for the whole machine. The engine powers the loader, enabling it to move and operate the loading functions. The bucket, attached to the lift arms, is used to scoop up materials. The wheels give it the ability to move swiftly and maneuver easily on different terrains, distinguishing it from other types of loaders.
- Versatility in Applications
Wheel loaders can be applied in multiple scenarios. In construction sites, they are used to load building materials onto trucks or to move debris. In mining operations, they help in loading ores and waste rocks. In agriculture, they can handle tasks like moving hay bales or loading fertilizers. Their adaptability makes them an essential piece of equipment in various workplaces.
II. Product Advantages
- High Reliability
-
- Quality Engine and Transmission System
Wheel loaders are equipped with reliable engines that have been rigorously tested. These engines are designed to provide stable power output under different working conditions, ensuring continuous operation without sudden breakdowns. The transmission system is also of high quality, with smooth gear shifting and efficient power transfer, enabling the loader to work effectively in various load-bearing situations.
-
- Robust Electrical and Hydraulic Systems
The electrical systems of wheel loaders are built to withstand harsh environments. They are protected against dust, moisture, and electrical interference, ensuring reliable operation of components such as lights, gauges, and control systems. The hydraulic systems are equally reliable, with high-performance hydraulic pumps and cylinders that can precisely control the movement of the bucket and lift arms, even under heavy loads.
-
- Proven Design and Manufacturing Standards
These loaders follow strict design and manufacturing standards. Their structures are carefully engineered to distribute stress evenly, reducing the risk of component failures. Years of research and improvement have gone into their design, resulting in a product that can be relied upon to perform consistently over time, meeting the demanding requirements of different industries.
- Good Durability
-
- High-Quality Materials
The materials used in the construction of wheel loaders are of top-notch quality. The chassis is made of sturdy steel that can withstand heavy loads and impacts. The bucket is often crafted from wear-resistant materials, such as high-strength steel alloys or special hardened steel, which can endure the abrasion caused by continuous contact with rough materials.
-
- Effective Anti-corrosion Measures
To enhance durability in various working environments, wheel loaders are equipped with effective anti-corrosion measures. Coatings and protective treatments are applied to key components to prevent rust and corrosion from moisture, chemicals, or other environmental factors. This extends the lifespan of the equipment and reduces maintenance costs over time.
-
- Regular Maintenance-friendly Design
The design of wheel loaders takes into account ease of maintenance. Components are easily accessible, allowing for quick inspections, replacements, and repairs. Regular maintenance tasks like changing oil, filters, and checking fluid levels can be done efficiently, ensuring that the loader remains in good working condition for a long period, further contributing to its durability.
- Strong Safety Features
-
- Operator Protection Cab
The cab of a wheel loader is designed as a safe haven for the operator. It is made of reinforced materials that can withstand impacts and protect the operator in case of accidents. The cab is also equipped with safety glass that is shatter-resistant and provides clear visibility. Inside the cab, there are comfortable seats with seat belts to ensure the operator's safety during operation.
-
- Stability and Anti-tip Mechanisms
Wheel loaders are designed with stability in mind. The wide wheelbase and low center of gravity contribute to its stable operation, reducing the risk of tipping over. Additionally, some models are equipped with anti-tip systems that can detect unstable conditions and automatically take corrective actions, such as limiting the movement of the bucket or reducing the speed, to keep the loader on a safe footing.
-
- Safety Warning Systems
To alert the operator of potential dangers, wheel loaders are equipped with various safety warning systems. These include audible alarms for when the loader is operating in reverse or when approaching its maximum load capacity. There are also visual indicators on the dashboard that show the status of key systems, allowing the operator to quickly identify and address any issues before they turn into safety hazards.
III. Product Operation Guide
- Pre-operation Checks
Before starting the wheel loader, conduct a thorough inspection. Check the tire pressure to ensure proper traction and stability. Examine the bucket for any visible damage or wear. Inspect the lift arms and their connections to make sure they are in good working condition. Also, check the engine oil level, coolant level, and hydraulic fluid level. Verify that all lights, gauges, and control levers are functioning properly.
- Starting the Wheel Loader
Sit in the operator's seat and fasten the seatbelt. Insert the key into the ignition switch and turn it to start the engine. Let the engine warm up for a few minutes while observing the instrument panel for any warning lights or abnormal readings. Once the engine is warmed up, you can begin operating the wheel loader.
- During Operation
Use the control levers to operate the wheel loader. The joystick or lever for the bucket controls its raising, lowering, and tilting movements. The other lever is used to control the movement of the lift arms. To move the wheel loader forward or backward, use the pedals for acceleration and braking. When loading materials, approach the pile slowly and position the bucket correctly to scoop up the materials smoothly. Avoid overloading the bucket to maintain the stability of the wheel loader.
- Post-operation Maintenance
After finishing the work, turn off the engine and let the wheel loader cool down. Clean the exterior of the loader, especially the bucket and tires, to remove any dirt, debris, or spilled materials. Check for any signs of wear or damage again and record any issues for maintenance. Follow the manufacturer's recommended maintenance schedule to perform regular maintenance tasks such as oil changes, filter replacements, and component inspections to keep the wheel loader in optimal working condition.